Projects
UBMM is dedicated to research of new theories, algorithms, and systems for multimedia encoding, transmission, adaptation, and authentication. It hosts faculty, students, and visiting researchers, conducting research as well as development of multimedia technologies and systems. Our topics include:
- 3D Video and Multiview Video Coding
- Secure and Reliable Multimedia over Wireless Networks
- Scalable Video over MIMO Wireless Networks
- Semantic-based Video Adaptation for Mobile Networks
- Environmental influence on mobile video perception
- Dependency graph based video bitstream watermarking
- Quality continuum model for HTTP adaptive video streaming
- Depth misalignment detection for color-plus-depth image
- Intelligent Interpolation and Upsampling for Image and Video
- Cross-layer Approaches to Robust Video over Wireless LAN
- Smart Network Coding for Multimedia over Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
- Model Guided Adaptive Human Motion Tracking from Video
 3D Video and Multiview Video Coding
3D Video and Multiview Video Coding
Three Dimensional Video (3DV), or Multiview Video (MVV), by definition, is a collection of signal that can provide depth perception of a given scene, from which at least stereo video will be rendered /displayed.
3DV has attracted significant interests recently both in industries and academics. Typical applications include 3D Television (3DTV) and Free Viewpoint Video (FVV), which have already incurred great attentions from the multimedia industry in recent years.
With FVV, viewers are able to choose any viewpoint in a 3D space for a given scene, while 3DTV can display stereo video (two views) or multiple views simultaneously for 3D perception.
In order to provide 3DV services, especially FVV service, supplemental data in addition to single 2D view sequence need to be transmitted, for example, video sequences of other views and depth signal of the corresponding scene. Compared to classical single view communication, the compression of the 3DV data is an incoming issue because of the huge data amount. We are looking into efficient compression of 3DV data, especially depth data now. Another incoming issue is transcoding, which should be developed to provide required service for different users in multimedia systems and extract useless views’ bitstream at the same time. Currently multiple views to single view transcoder has been finished, where inter-view reference’s information is used in transcoding.
Participant:
Shujie Liu
 Secure and Reliable Multimedia over Wireless Networks
Secure and Reliable Multimedia over Wireless Networks
The challenging issue of ensuring both reliable and secure transmission of multimedia data over wireless networks still remains open. For security, we focus on the media authentication which includes both source identification and content verification.
Our research mainly focuses on the stream level layered joint design of source coding, channel coding and authentication to minimize additional computation/authentication overhead and provide optimal end-to-end media quality.
This project has already generated two conference papers (best student paper finalist, ICME 2009; ICME 2010) and one journal paper submitted to ACM TOMCCAP.
Participant:
Xinglei Zhu
 Scalable Video over MIMO Wireless Networks
Scalable Video over MIMO Wireless Networks
Antenna selection is a technique in MIMO networks to reduce number of antennas used and therefore reduce the cost of multiple RF chains. When transmitting scalable video over such MIMO networks, antenna selection should consider the received quality of transmitted video.
Our research mainly focuses on antenna selection for scalable video and MIMO, which is a kind of cross-layer design.
Participants:
Shujie Liu
Qian Liu
 Semantic-based Video Adaptation for Mobile Networks
Semantic-based Video Adaptation for Mobile Networks
With user’s guidance, developing semantic based consumer photo adaptation schemes to accommodate the variation of resource constraints and limitation of capabilities of mobile devices in heterogeneous networks.
In this project we explore visual cues and semantic concepts in the content of consumer photos and design the semantic based adaptation scheme to achieve optimal adaptation result to improve end users’ perceptual experience under various resource constraints.
In particular, the research mainly focuses on the following aspects:
Participant:
Wenyuan Yin
 Environmental influence on mobile video perception
Environmental influence on mobile video perception
 Different from television and monitor watching, the viewing of mobile displays is significantly influenced by the surrounding environment of the wireless device.
It is our interest to quantize and utilize such viewing contexts.
First, the viewing factors (display device size, ambient luminance, motion of viewer) are enumerated. Their influence on video viewing is measured by subjective test and modeled. Based on the result, a quality metric (MJND) is derived to estimate visual quality of a video content under a certain environment. The validation result shows the proposed model accurately predicts MOS (subjective quality) with busy context (PCC > 0.9). In addition, a video transcoding approach is proposed to dynamically tailor video bitstream to optimize the viewing quality according to the viewing environment. We implemented a transcoder for H.264. Based on the preliminary results, the transcoding can save up to 30% bitrate for users in a busy context. We also propose to apply such transcoder in multi user resource allocation.
Different from television and monitor watching, the viewing of mobile displays is significantly influenced by the surrounding environment of the wireless device.
It is our interest to quantize and utilize such viewing contexts.
First, the viewing factors (display device size, ambient luminance, motion of viewer) are enumerated. Their influence on video viewing is measured by subjective test and modeled. Based on the result, a quality metric (MJND) is derived to estimate visual quality of a video content under a certain environment. The validation result shows the proposed model accurately predicts MOS (subjective quality) with busy context (PCC > 0.9). In addition, a video transcoding approach is proposed to dynamically tailor video bitstream to optimize the viewing quality according to the viewing environment. We implemented a transcoder for H.264. Based on the preliminary results, the transcoding can save up to 30% bitrate for users in a busy context. We also propose to apply such transcoder in multi user resource allocation.
Participant:
Jingteng Xue
 Dependency graph based video bitstream watermarking
Dependency graph based video bitstream watermarking
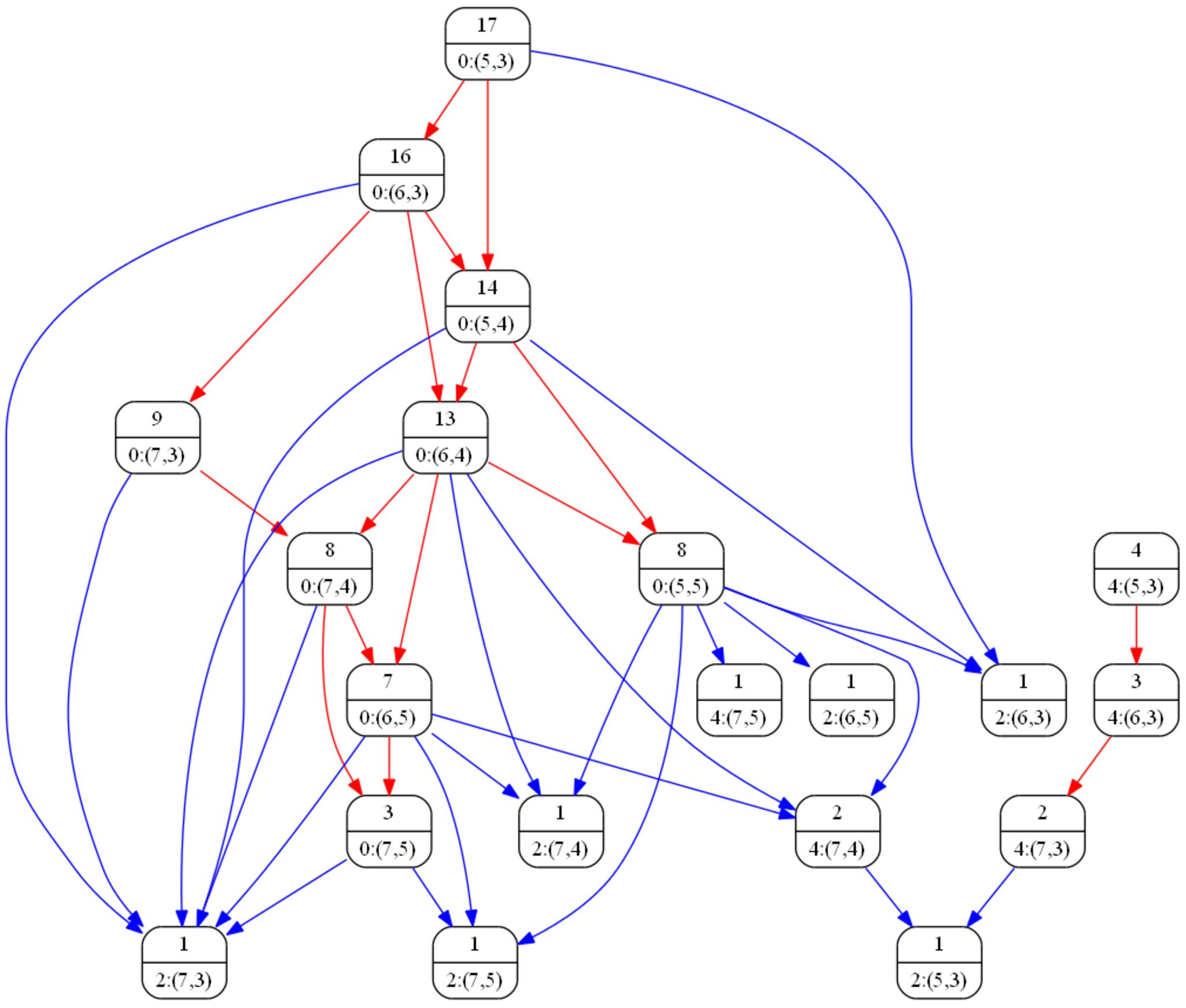 Video watermarking is a powerful and important tool in content protection systems. The invisible yet robust watermark protects video content from illegal distribution. However the injection of watermark may cause visual artifacts or complex computation that removes such artifacts. We propose a novel watermarking scheme based on a topology sort of the proposed coding prediction dependency graph. In this way, the embedding process of watermark can minimize error propagation compensation and therefore cost very light computation. In addition, the proposed approach optimizes viewing quality since the visibility of prediction error is minimized. Besides watermarking, the dependency graph and the topology sort based macro block selection is useful in many applications.
Video watermarking is a powerful and important tool in content protection systems. The invisible yet robust watermark protects video content from illegal distribution. However the injection of watermark may cause visual artifacts or complex computation that removes such artifacts. We propose a novel watermarking scheme based on a topology sort of the proposed coding prediction dependency graph. In this way, the embedding process of watermark can minimize error propagation compensation and therefore cost very light computation. In addition, the proposed approach optimizes viewing quality since the visibility of prediction error is minimized. Besides watermarking, the dependency graph and the topology sort based macro block selection is useful in many applications.
Participant:
Jingteng Xue
 Quality continuum model for HTTP adaptive video streaming
Quality continuum model for HTTP adaptive video streaming
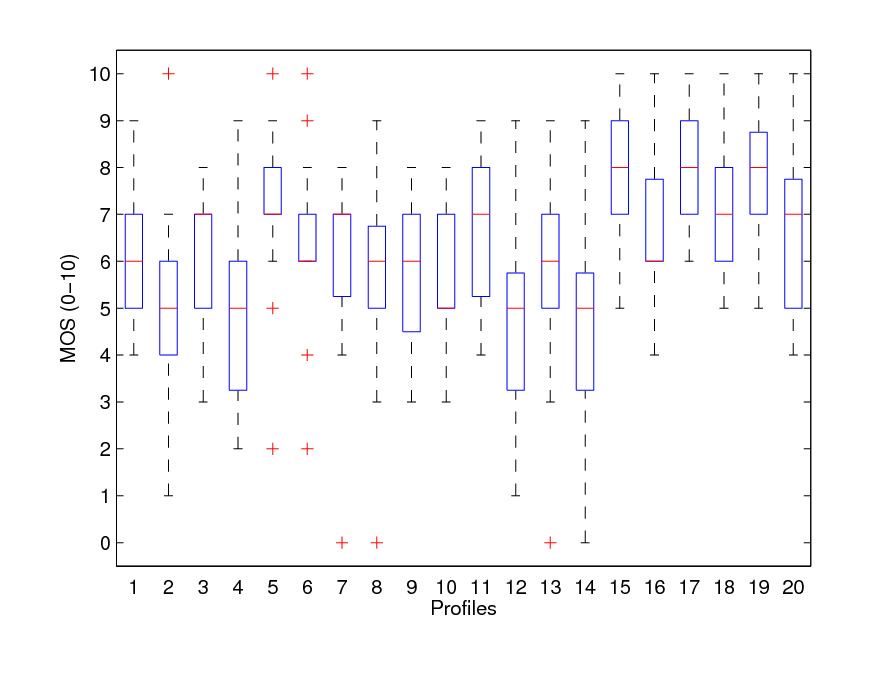 In HTTP adaptive streaming, when the bandwidth is insufficient, the decoder can choose to pause the playback and rebuffer content or dynamically select segments with smaller bitrate. It is a major unsolved problem to understand the tradeoff. We propose two new concepts: instantaneous quality and cumulative quality. We derive a novel parametric model to estimate the instantaneous quality and then get cumulative quality by temporally pooling instantaneous quality based on forgetting curve property of human memory. Hence the temporal and spatial distortion can be simultaneously addressed with very light computation cost. The model is validated by a dataset of 20 profiles. The result shows an average correlation of 0.82, which is better than conventional benchmarks. The model can be used in many applications including live HTTP streaming monitoring and decoder segment selection etc.
In HTTP adaptive streaming, when the bandwidth is insufficient, the decoder can choose to pause the playback and rebuffer content or dynamically select segments with smaller bitrate. It is a major unsolved problem to understand the tradeoff. We propose two new concepts: instantaneous quality and cumulative quality. We derive a novel parametric model to estimate the instantaneous quality and then get cumulative quality by temporally pooling instantaneous quality based on forgetting curve property of human memory. Hence the temporal and spatial distortion can be simultaneously addressed with very light computation cost. The model is validated by a dataset of 20 profiles. The result shows an average correlation of 0.82, which is better than conventional benchmarks. The model can be used in many applications including live HTTP streaming monitoring and decoder segment selection etc.
Participant:
Jingteng Xue
 Depth misalignment detection for color-plus-depth image
Depth misalignment detection for color-plus-depth image
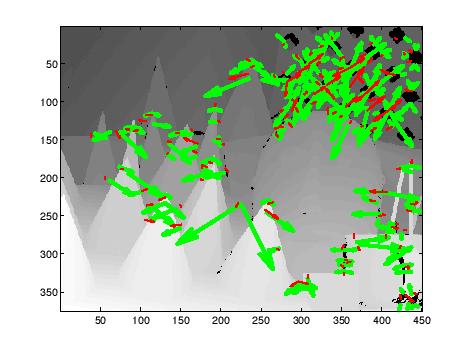 Depth-image-based rendering (DIBR) is a popular 3D video viewing approach. In color-plus-depth format, the depth information can be either measured by IR sensors or derived from stereo-pair images by computer vision algorithms but the depth acquisition/estimation and coding process is error-prone. The displacement distortion of depth, especially the misalignment around the object edges, may cause ghosting and flickering during 3D playback. In order to improve perception quality, we propose to estimate the depth map quality and detect the potential problematic depth information by matching co-located feature points in texture and depth image. The misaligned depth is reported for correction and further processing.
Depth-image-based rendering (DIBR) is a popular 3D video viewing approach. In color-plus-depth format, the depth information can be either measured by IR sensors or derived from stereo-pair images by computer vision algorithms but the depth acquisition/estimation and coding process is error-prone. The displacement distortion of depth, especially the misalignment around the object edges, may cause ghosting and flickering during 3D playback. In order to improve perception quality, we propose to estimate the depth map quality and detect the potential problematic depth information by matching co-located feature points in texture and depth image. The misaligned depth is reported for correction and further processing.
Participant:
Jingteng Xue
 Cross-layer approaches to robust video transmission over wireless LAN
Cross-layer approaches to robust video transmission over wireless LAN
Video transmission over wireless LAN has challenges to guarantee the quality of service (QoS) with packet loss due to instable
wireless channel. Previous work to address this issue mainly focused on video coding schemes, namely on application layer. Recently, cross-layer approaches are booming since wireless LAN starts to provide QoS support on MAC layer. These cross-layer
approaches seek a optimal solution by combining multiple layers consideration. For example, video coding schemes on application layer, route discovery on network layer, differentiation-aware transmitting on MAC layer and channel conditions on physical layer
can be taken into account together to design a good cross-layer approach. Cross-layer approaches are demonstrated to improve quality of video transmission over wireless LAN dramatically.
Participant:
Jianchao Du
 Model guided adaptive human motion tracking from video
Model guided adaptive human motion tracking from video
Human motion tracking is useful in biomechanical and clinical analysis, HCI and so on. Because video based human motion tracking does not need attaching auxiliary instruments on human body, it is more convenient and feasible to tracking human motions in many applications.
The research challenges of this problem include but not limit to addressing the complex nature of human motion and self occlusion. In this project we focus on model guided adaptive human motion tracking schemes. We define 2D/3D hierarchical models of human body and build up
a model of constraints of human motion based on training set. We further combine image features with the motion model to carry out adaptive tracking.
Participant:
Lifang Wu
 Smart network coding for multimedia over heterogeneous wireless Networks
Smart network coding for multimedia over heterogeneous wireless Networks
Network coding is proved to be an efficient tool to improve network throughput. However, traditional network coding is designed for best effort transmission without considering the traffic's QoS constraints. This project aims to unveil
the intrinsic relationship between network coding and QoS (e.g. delay, packet loss). Coding theory, queueing theory, and graph theory are main mathematical tools for this project. Results from this project can be applied to video/audio streaming over wireless networks, especially in heterogeneous wireless networks,
in which different access networks support different QoS levels, for example, a 3G cellular networks with random access WiFi relays.
Participant:
Wei Pu
 Intelligent Interpolation and Upsampling for image and Video
Intelligent Interpolation and Upsampling for image and Video
Intelligent interpolation and up-sampling for image and video is a technique to produce a higher resolution version of given images and video streams. The current popular interpolation methods can not give out high
quality both subjective and objective. Furthermore most of them are very complicated. Our approach takes the full advantages of frequency-domain and spatial-domain interpolations. It can produce higher objective quality
and subjective quality at the same time.
Participant:
Zhenyu Wu



 Back to top
Back to top