Embedded Systems
Embedded System Design
Lets compare an embedded system with a general purpose system.
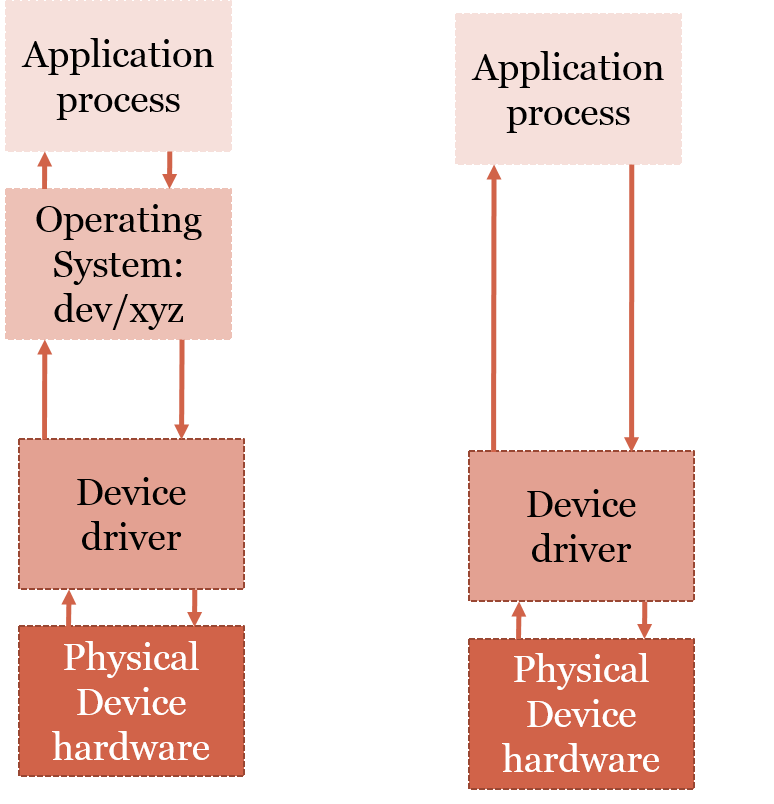 In a typical embedded system, the apps or applications are directly interfacing with the hardware. The embedded software is optimized to work with
the embedded hardware. Common embedded system design involves simple representation such as UML (Unified Modeling Language) state machine.
In a typical embedded system, the apps or applications are directly interfacing with the hardware. The embedded software is optimized to work with
the embedded hardware. Common embedded system design involves simple representation such as UML (Unified Modeling Language) state machine.
An FSM M = five tuple { S, i, T, Σ, δ }
S = set of states
i = initial state
T = terminal state (s)
Σ = events that bring about transitions
δ = transitions
Embedded System design:You begin the design process by examining the problem description, the requirements stated in there, and then move on to design repesentation, build the prototype, test it and finally build the production system.
Problem--> requirements--> design--> prototype--> test--> final system.
Lets look at some simple examples.
Problem 1: Automatic vending machine money counter Introduction:Embedded system (25Cent counter) Input:Coins: 5, 10, 25 cent coins output:Light turns on when count (total of coins input) reaches 25 or over
Design:FSM1
Problem 2: Drone avionics
Introduction: Is given in the form of an FSM.

Input: Commands or events triggering drone action
Output:Action of the drone
Design: FSM2 above
We will use two approaches (i) function-driven and (ii) table-driven to arrive at the solution for this problem. We will discuss the pros and cons of these two approaches for designing embedded systems.